

- #Standard deviation rstudio for free#
- #Standard deviation rstudio how to#
- #Standard deviation rstudio install#
- #Standard deviation rstudio code#
To avoid this, you can use the read.csv() command to read in the data, specifying within the command whether each of the variables should be quantitative (“numeric”) or categorical (“factor”). It is common for factors to be read as quantitative variables when importing a dataset into R. The only difference between the different analyses is how many independent variables we include and in what combination we include them. We will use the same dataset for all of our examples in this walkthrough. Note that this data was generated for this example, it’s not from a real experiment. Library(AICcmodavg) Step 1: Load the data into R Then load these packages into your R environment (do this every time you restart the R program): library(ggplot2)
#Standard deviation rstudio install#
Install and load the packagesįirst, install the packages you will need for the analysis (this only needs to be done once): install.packages(c("ggplot2", "ggpubr", "tidyverse", "broom", "AICcmodavg")) To run the code, highlight the lines you want to run and click on the Run button on the top right of the text editor (or press ctrl + enter on the keyboard).
#Standard deviation rstudio code#
Now you can copy and paste the code from the rest of this example into your script. Once you have both of these programs downloaded, open R Studio and click on File > New File > R Script. If you haven’t used R before, start by downloading R and R Studio.
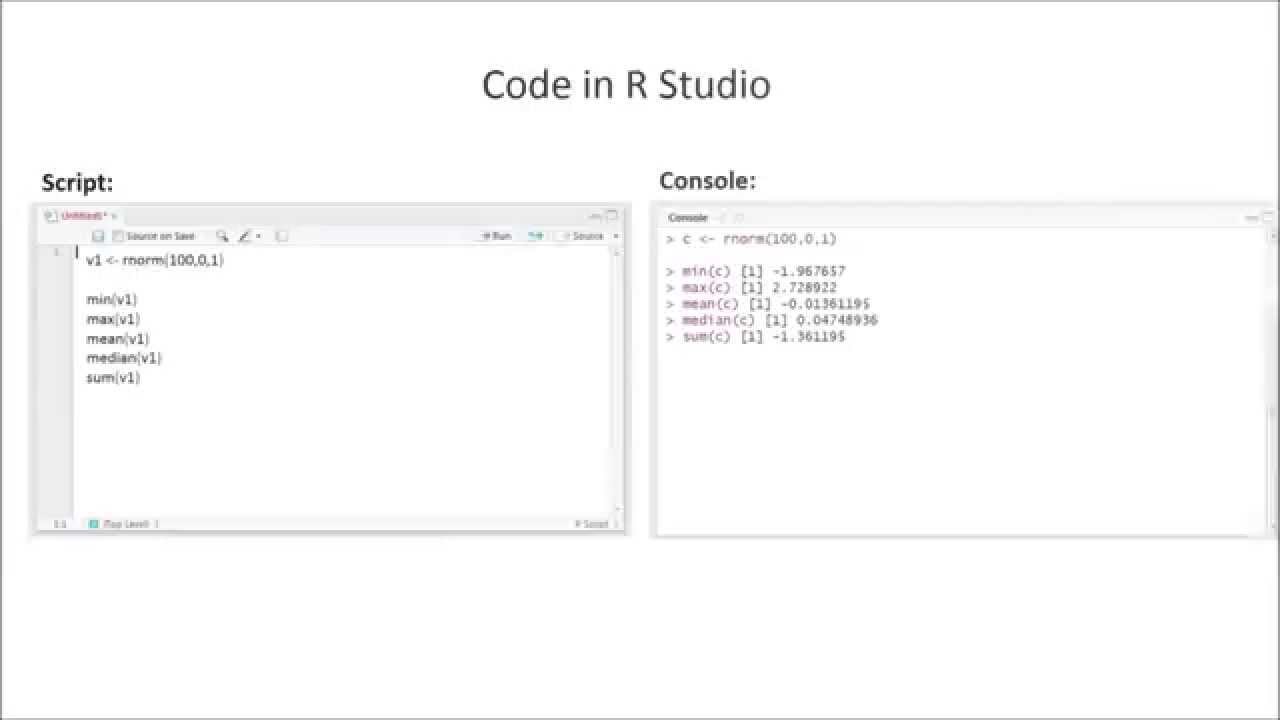
#Standard deviation rstudio how to#
We will also include examples of how to perform and interpret a two-way ANOVA with an interaction term, and an ANOVA with a blocking variable. We test the effects of 3 types of fertilizer and 2 different planting densities on crop yield. Two-way ANOVA exampleIn the two-way ANOVA, we add an additional independent variable: planting density. One-way ANOVA exampleIn the one-way ANOVA, we test the effects of 3 types of fertilizer on crop yield. Our sample dataset contains observations from an imaginary study of the effects of fertilizer type and planting density on crop yield. In this guide, we will walk you through the process of a one-way ANOVA (one independent variable) and a two-way ANOVA (two independent variables). The null hypothesis ( H 0) of the ANOVA is no difference in means, and the alternative hypothesis ( H a) is that the means are different from one another. ANOVA tests whether there is a difference in means of the groups at each level of the independent variable.
#Standard deviation rstudio for free#
Try for free ANOVA in R | A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with ExamplesĪNOVA is a statistical test for estimating how a quantitative dependent variable changes according to the levels of one or more categorical independent variables. When I plug this sd in qnorm(.95,mean=32,sd=3.0), I get a value of 36.Eliminate grammar errors and improve your writing with our free AI-powered grammar checker.
Then I verified that I get the upper bound by using: qnorm(.95,mean=32,sd=3.64774) = 38Īccording to Empirical rule,95% of the data falls within 2 standard deviations of the mean StDev = 3.64774 (expected answer is to be rounded to one decimal) The mean + 1.644854 standard deviations is 38 (95% of customers save no more than this)ģ8 - 32 = 6 (this is equal to 1.644854 StDev) METHOD 1: Found Z score using qnorm(0.95) If you were to model this expert's opinion using a normal distribution (by applying empirical rule), what standard deviation would you use for your normal distribution? (round your answer to 1 decimal place.Ĭan someone suggest what is the correct method of solving this problem? Please provide R script Using the R script solve the following: An expert on process control states that he is 95% confident that the new production process will save between $26 and $38 per unit with savings values around $32 more likely.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
